- MPFA
-
MPF System
- Background
- Types of MPF Schemes
- MPF Coverage
- Enrolment and Termination
- Mandatory Contributions
- Voluntary Contributions / Tax Deductible Voluntary Contributions
- MPF Tax Matters
- MPF Account Management
- Withdrawal of MPF
- Arrangements for Offsetting Long Service Payment and Severance Payment
- Anniversaries of MPF System
- MPF Investment
- ORSO
- Supervision
- Enforcement
- eMPF Platform

Info Center
Press Releases
- Your Position
- Homepage
- Information Centre
- Press Releases
- MPFA blog - 24 Years of MPF
Share
-
Facebook
-
LinkedIn
-
WhatsApp
-
Email
-
Copy Address
URL copied! -
Print This Page
MPFA blog - 24 Years of MPF
MPFA Chairman Mrs Ayesha Macpherson Lau published her blog post on the 24th anniversary of the MPF System (the MPF) today (1 December). She highlighted that two-thirds of Hong Kong’s working population, especially grassroots employees, had no occupational retirement protection before the implementation of the MPF, but the retirement protection coverage for the workforce now is close to 100%. Compared to some occupational pension systems in other regions, the design of the MPF is forward-looking and inclusive, with extensive coverage, including both general employees and self-employed persons and casual workers in specific industries.
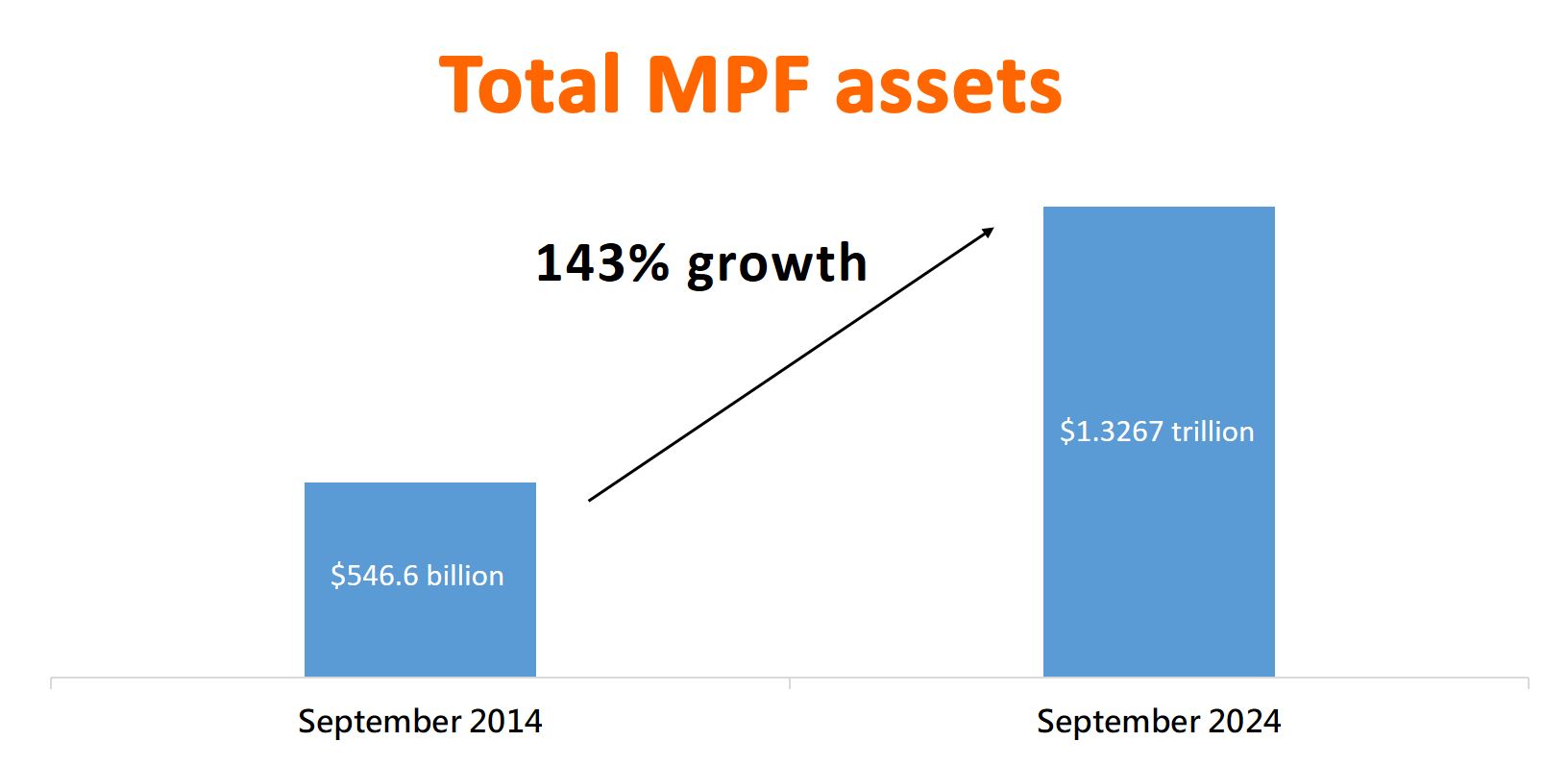
Mrs Lau cited a series of figures in her blog post to illustrate the effectiveness of the MPF in providing basic retirement protection for the working population. As of September 2024, the total assets of the MPF exceeded $1.32 trillion, which is a 143% increase over that 10 years ago. It is a sustainable and important resource for basic retirement protection, unaffected by continued population ageing and the public finance situation.
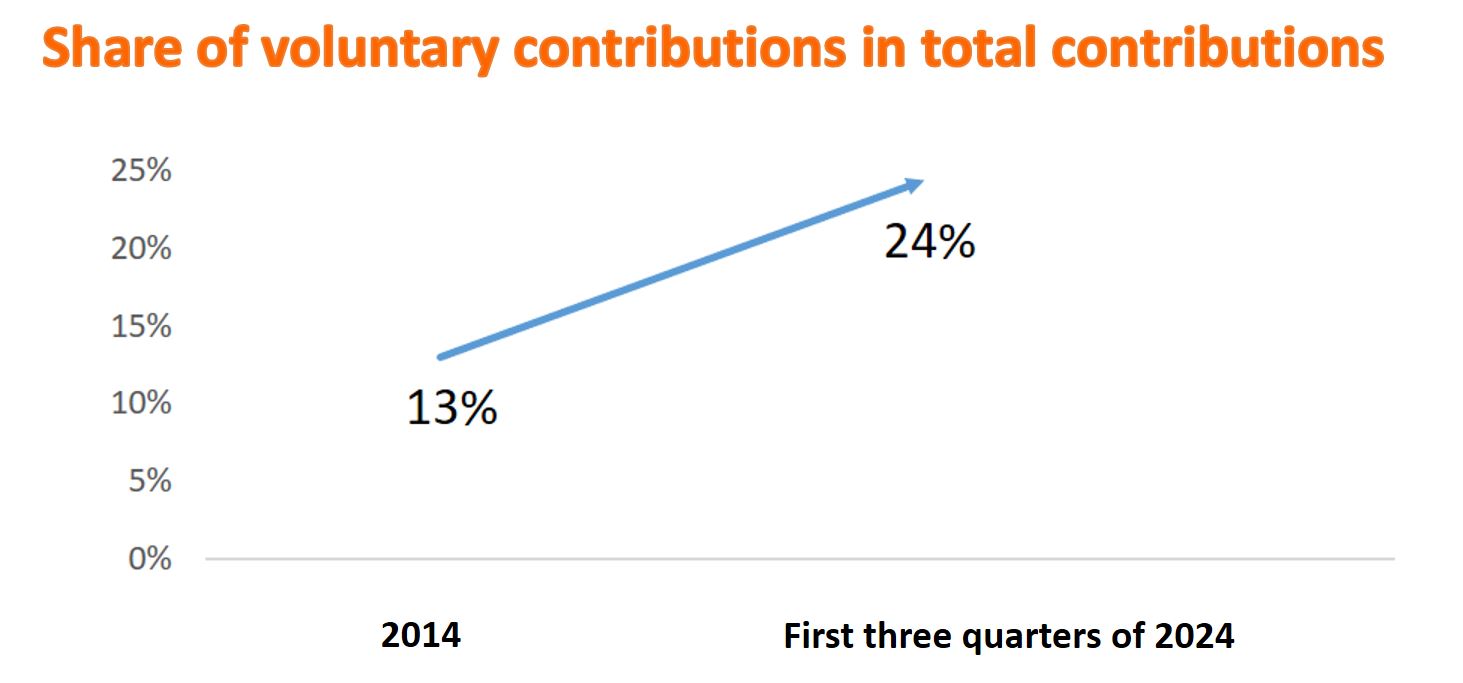
Mrs Lau also pointed out that voluntary contributions by employers and employees is one way to effectively enhance the adequacy of the MPF. In 2014, voluntary contributions made by employers and employees accounted for 13% of total contributions. Following the gradual increase in their share in total contributions over the past 10 years, and with the introduction of tax-deductible voluntary contributions (TVC) in April 2019, these voluntary contributions made up 24% of the total contributions in the first three quarters of 2024.
Additionally, one-third of employee contribution accounts that have been opened since 2000 (i.e. the inception of the MPF) and continue to receive contributions have voluntary contributions. The average accumulated MPF assets in these accounts is about $1.1 million, demonstrating the effectiveness of voluntary contributions in enhancing retirement protection.
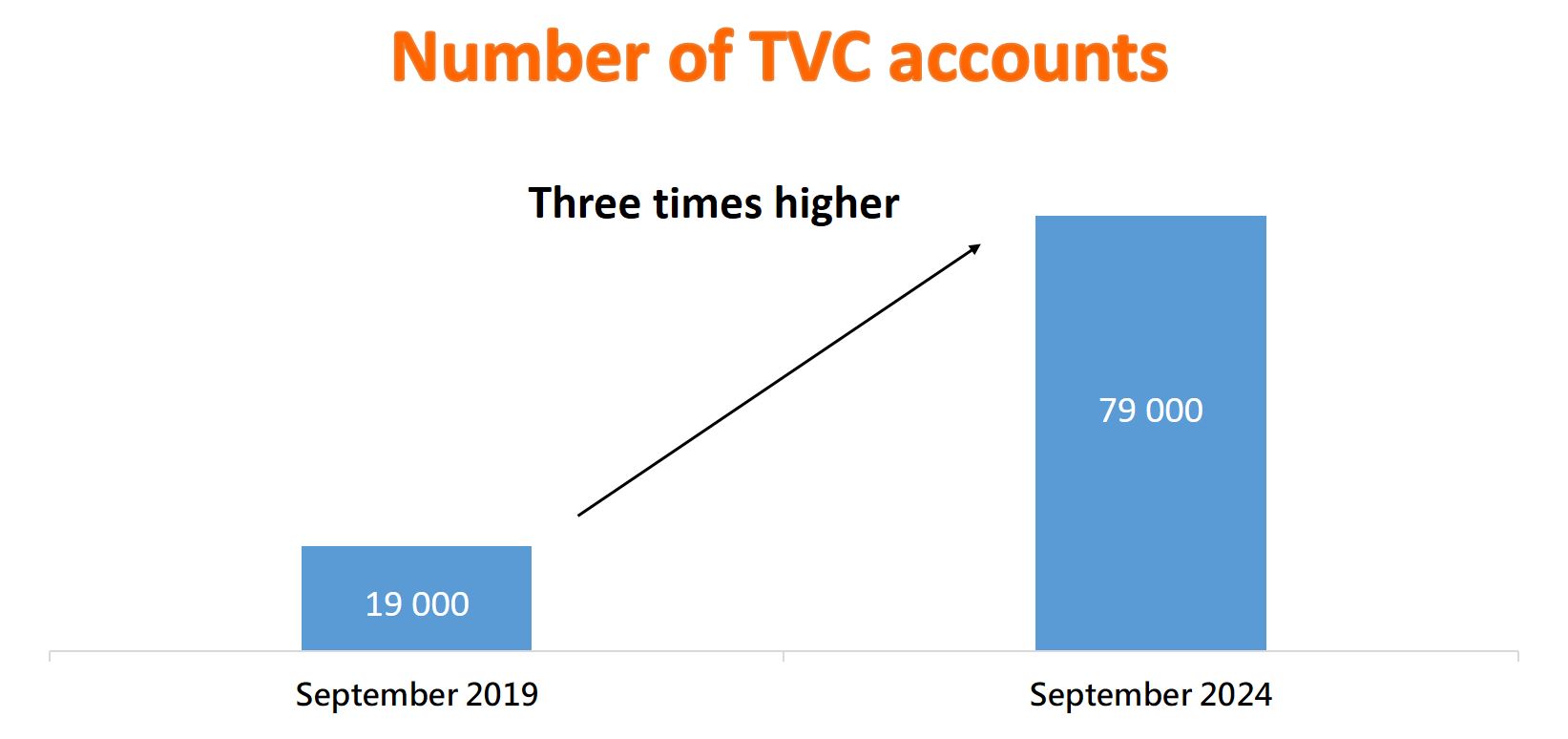
TVC is popular with many scheme members because it can further enhance their retirement protection while providing them with tax deductions. As of September this year, the number of TVC accounts totaled 79,000, which is three times higher than the 19,000 accounts during the same period five years ago. As at the end of September this year, the cumulative contributions received exceeded $11 billion.
Mrs Lau mentioned that the MPFA launched the default investment strategy (DIS) in 2017 having considered that some employees may not have time or knowledge to manage their MPF investments. Since its launch on 1 April 2017 till September this year, the core accumulation fund under the DIS achieved an average annualized net return of 6.4%, far exceeding the annualized inflation rate (1.9%) during the same period and outperforming other fund types (0.5% – 5.1%). The DIS follows the principle of diversified investment in global markets and assets, and the fees of DIS funds are capped at 0.95% of the net asset value of the funds. The cap will be reduced to 0.85% after an MPF scheme has onboarded the eMPF Platform (the eMPF). This will help enhance the net investment returns and adequacy of the MPF.
Another measure to enhance the adequacy of the MPF is to review the sufficiency of the contribution levels. The MPFA is conducting a review of the minimum and maximum relevant income levels for MPF contribution for the 2022–2026 cycle, and will submit a proposal to the Government as soon as the review is completed.
Mrs Lau stated that more reforms to enhance the MPF are in the pipeline, namely, (1) the effect of fee reductions resulting from the operation of the eMPF since June this year, which have gradually materialized; (2) the Government’s implementation of the abolition of the MPF “offsetting” arrangement on 1 May next year, which will further enhance the retirement savings of employees; and (3) the completion of the formulation of detailed proposals for “full portability” of MPF benefits and legislative amendments within next year, to facilitate its launch as soon as possible after the full operation of the eMPF, providing the working population with greater flexibility in managing their MPF, enhancing market competition, and creating room for further fee reductions.
For the full version of the post, please visit the MPFA blog. The blog is in Chinese only.
-Ends-
1 December 2024

